Differences between Presbyopia and Hyperopia
Mar 27, 2012
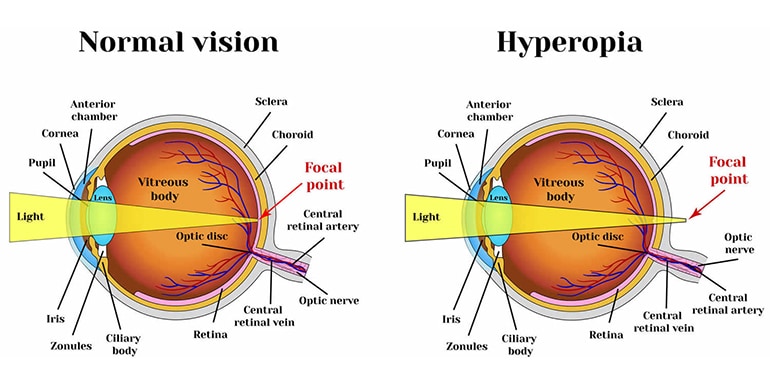
In common cases, people are confused with presbyopia and hyperopia and assume that they are the same. The patients of presbyopia and hyperopia both have obstacles to reading and fine work, and both need to wear corrective glasses. Presbyopia and hyperopia actually two different eye problems.
1. Different purposes of wearing glasses
Presbyopia patients wear the glasses for the purpose of correcting the lag and lack of myopia adjustment. It means that when doing reading, writing or fine work at near distances, people need to wear suitable eyeglasses to help improve the adjustment abilities that work needs.
In comparison, the correction of hyperopia is the purpose of wearing glasses and the glasses need to be worn in everyday life.
2. Differences in causes
Presbyopia is the declining of near eyesight caused by loss of elasticity due to the hardening of the lens, gradually weakened ciliary muscle contraction and thus regulation failure and decreased ability for adjustment. It is a special physiological state of refractive errors that may happen to everyone; thus it cannot be considered as pathological problems or refractive errors.
On contrast, hyperopia is a kind of refractive error that is caused by a variety of reasons, featuring too small eye refractive power or too short eye axis distance. It is a pathological phenomenon that requires regulatory function whether looking far or near.
3. Differences in Clinical Symptoms
Presbyopia is a disease that only those people over 40 have exclusively. The main symptoms are that the eyes switch from near to distance when doing reading or fine work, which also cannot be sustained. As age increases, the symptoms get worse gradually but the hyperopia eyesight remains normal or has no significant effects.
However, hyperopia can occur at any age, and it is often there after birth. Hyperopia patients cannot see distant objects clearly and more vague for near objects, while some symptoms can be improved by correction (mild hyperopia, younger or people with strong correction abilities, can compensate for the refractive defect strengthening self-regulation), and get normal distance vision (under corrective treatment).
Knowing the differences between presbyopia and hyperopia first is the key foundation of correcting the eye problems. Remember to wear the right eyeglasses for your eyes.